学习内容
- 了解J.U.C
- Lock的基本使用
- ReentrantLock重入锁
- AQS原理分析
- AQS源码分析
J.U.C
j.u.c(java.util.concurrent)是java并发编程工具包包,
像concurrentMap、BlockingQueue、Lock、AbstractOwnableSynchronizer等等都是该包下的类(接口)
Lock的基本使用
@Data
public class UseLock {
static ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
static ReentrantReadWriteLock readWriteLock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock();
private static int num = 0;
private static int count = 10;
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
// lock.lock();
for (int i1 = 0; i1 < 1000; i1++) {
num ++;
}
// lock.unlock();
}).start();
}
Thread.yield();
System.out.println(num);
}
}
ReentrantLock(重入互斥锁)
什么是重入锁?
重进入是指任意线程在获取到锁之后,再次获取该锁而不会被该锁所阻塞。
每个锁都关联了一个线程持有者和计数器。
线程再次获取锁:锁需要识别获取锁的现场是否为当前占据锁的线程,如果是,则再次成功获取;释放锁时计数器自减,当计数器为0时,锁释放成功。
其它线程请求该锁,则必须等待;而该持有锁的线程如果再次请求这个锁,就可以再次拿到这个锁。
ReentrantLock 构造器的一个参数是 boolean 值,它选择想要一个 公平锁,还是不公平锁。公平锁使线程按照请求锁的顺序依次获得锁。
TryLock():当获取锁时,如果其他线程持有该锁,无可用锁资源,直接返回false,这时候线程不用阻塞等待,可以先去做其他事情;
/**
* @PackageName: com.raven.multithreaded.thoroughlock
* @ClassName: ReentrantLockTest
* @Blame: raven
* @Date: 2021-08-24 20:57
* @Description: 重入锁
*/
public class ReentrantLockTest {
/**
* 锁对象是ReentrantLockTest 对象 线程调用获取锁对象
*/
public synchronized void demo() {
System.out.println("demo");
demo2();
}
public void demo2(){
// 锁对象是ReentrantLockTest 对象
// 再次获取锁对象
// 增加重入次数
synchronized (this){
System.out.println("demo2");
} // 减少重入次数
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ReentrantLockTest test = new ReentrantLockTest();
test.demo();
}
}
synchronized 和 reentrantlock都是支持重入的!
Reentrentlock 实现过程
public class ReentrantLockUse {
static ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
public static void main(String[] args) {
lock.lock();
System.out.println("do sth");
lock.unlock();
}
}
类图引用关系
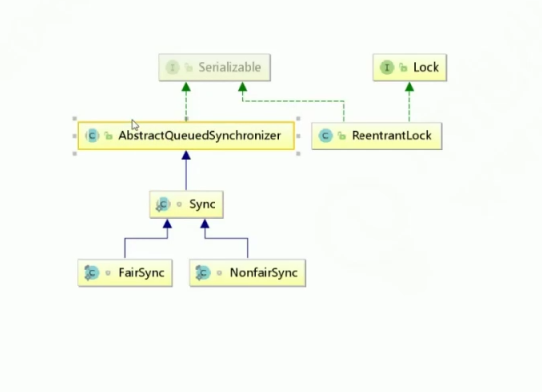
Lock.lock()-UML时序图
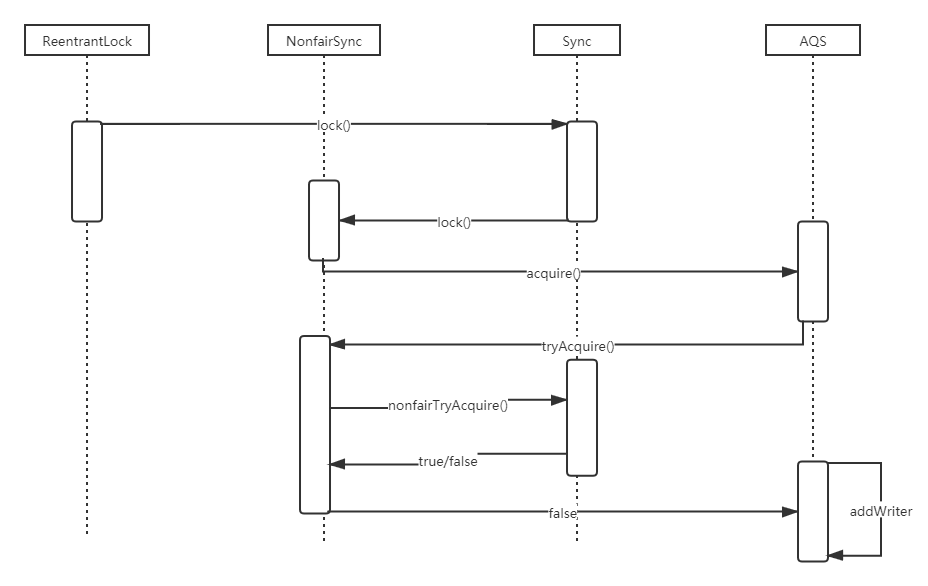
基于ReentrantLock进行AQS源码分析
// ReentrantLock.class
lock.lock();
// 调用sync的lock方法
public void lock() {
// lock()方法是一个抽象方法
sync.lock();
}
// **************************************************************************************
// NonfairSync.class
// sync.lock()是一个抽象方法,真正的实现是由NonfairSync/fairSync完成
final void lock() {
// 通过cas(比较并交换)的方式判断是否有线程拥有锁,如果没有任何线程占有锁,则将当前线程设置为占有锁
// 线程状态:
// static final int RUNNING = 0;
// static final int COMPLETING = 1;
// static final int COMPLETED = 2;
// static final int CANCELLED = 4;
// static final int INTERRUPTED = 8;
if (compareAndSetState(0, 1))
setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread());
else
// 如果已经有线程占有锁,则调用AQS的acquire方法捕获这个线程
acquire(1);
}
// 调用底层C++代码进行cas比较
protected final boolean compareAndSetState(int expect, int update) {
// See below for intrinsics setup to support this
return unsafe.compareAndSwapInt(this, stateOffset, expect, update);
}
// 设置当前线程独占锁
protected final void setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread thread) {
exclusiveOwnerThread = thread;
}
// **********************************************************************************
// AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.class
// 当线程尝试获取锁识别后,构建一个双向链表的数据结构,将该线程加入双向链表
public final void acquire(int arg) {
// 因为是非公平锁,所以会调用NonfairSync的tryAcquire方法尝试再次获取锁,如果占有锁的线程已经释放锁,就之前抢占锁
// 通过AQS的addWaiter方法 使用独占的方式将当前的线程封装成Node,然后构建链表
// 通过AQS的acquireQueued,最终挂起线程
if (!tryAcquire(arg) && acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg)){
// 执行唤醒后的线程的中断方法
selfInterrupt();
}
}
// NonfairSync.class
// 调用NonfairSync的tryAcquire方法,再次尝试获取线程,当之前占有锁的线程释放锁后,直接获取锁。
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
return nonfairTryAcquire(acquires);
}
// Sync.class
final boolean nonfairTryAcquire(int acquires) {
// 根据当前线程的状态判断当前线程是否可以占有锁 通过CAS进行判断
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
if (c 0) {
//如果可以占有锁,则设置当前线程独占锁
if (compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
}
// 因为Lock锁是可重入锁,所以判断已经占有锁的线程是不是当前线程,如果是当前线程,则记录重入次数。
else if (current getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {
int nextc = c + acquires;
if (nextc < 0) // overflow
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
return false;
}
// CAS设置
protected final boolean compareAndSetState(int expect, int update) {
// See below for intrinsics setup to support this
return unsafe.compareAndSwapInt(this, stateOffset, expect, update);
}
protected final void setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread thread) {
exclusiveOwnerThread = thread;
}
// *****************************************************************************************
// AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.class
// 使用独占的方式将当前的线程封装成Node,然后构建链表并返回当前节点
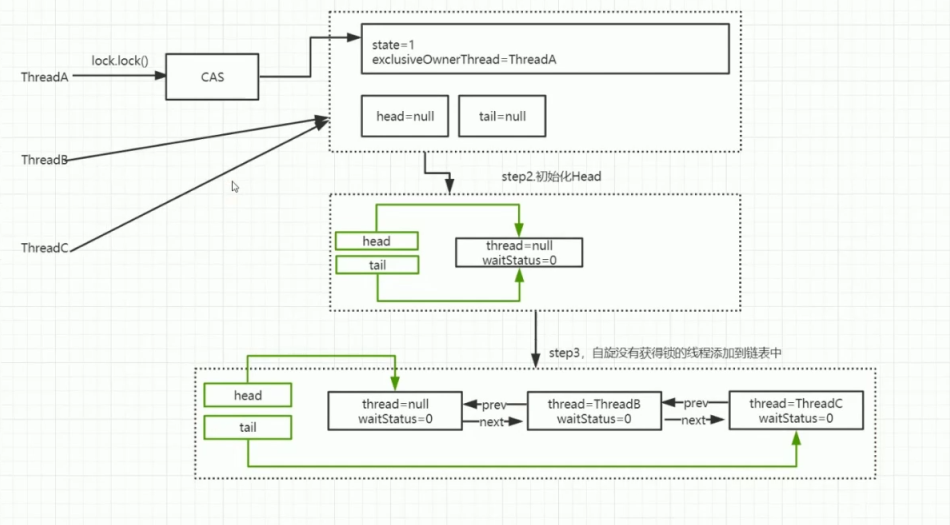
private Node addWaiter(Node mode) {
// 将当前线程封装为Node
Node node = new Node(Thread.currentThread(), mode);
// Try the fast path of enq; backup to full enq on failure
// 将pred 设置为 tail
Node pred = tail;
// 当线程首次进入时 pred为null,直接进入enq的逻辑
// 当pred预定义的节点不为空时 设置当前节点的属性,将当前节点和预定义节点头尾关联
if (pred != null) {
node.prev = pred;
if (compareAndSetTail(pred, node)) {
pred.next = node;
return node;
}
}
// 设置node节点的属性
enq(node);
return node;
}
// 通过自旋的方式设置node节点的属性
private Node enq(final Node node) {
for (;;) {
// 线程首次进入时,直接通过enq自旋的方式设置节点的属性,构造一个空节点
// tail 和 head 都是这个空节点
Node t = tail;
if (t null) { // Must initialize
if (compareAndSetHead(new Node()))
tail = head;
} else {
// 自旋 第二次进入,将空节点和当前线程封装好的节点链接
// 设置当前节点的prev 为空节点
node.prev = t;
// 将当前节点设置为tail
if (compareAndSetTail(t, node)) {
// 设置空节点的next为为当前节点
t.next = node;
return t;
}
}
}
}
private final boolean compareAndSetTail(Node expect, Node update) {
return unsafe.compareAndSwapObject(this, tailOffset, expect, update);
}
// *************************************************************************************
// AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.class
// 处理当前节点,当前线程再次尝试获取锁,如果没抢到锁则阻塞挂起
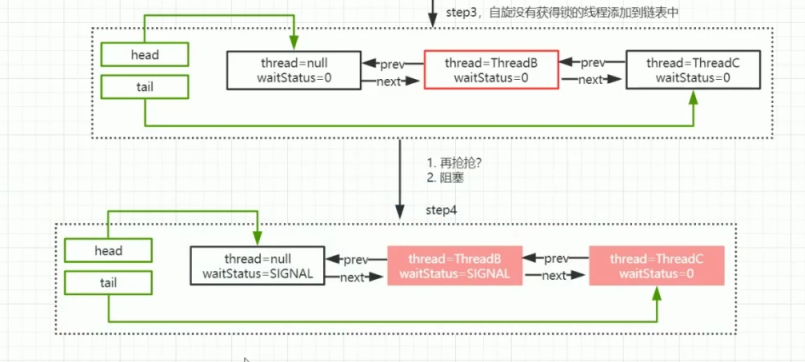
final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) {
boolean failed = true;
try {
boolean interrupted = false;
for (;;) {
//获取当前节点的上一个节点
final Node p = node.predecessor();
// 如果上一个节点是head,并且当前占有锁的线程已经释放锁,争抢锁成功
// 把当前节点设置为head,将之前的head节点脱离列表
if (p head && tryAcquire(arg)) {
setHead(node);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return interrupted;
}
// 如果争抢锁失败后 判断是否需要挂起线程
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) && parkAndCheckInterrupt()){
interrupted = true;
}
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
// 判断是否需要挂起线程 并标注前置节点状态为single
private static boolean shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(Node pred, Node node) {
// 获取前置节点的状态
int ws = pred.waitStatus;
// static final int CANCELLED = 1;
// /** waitStatus value to indicate successor's thread needs unparking */
// static final int SIGNAL = -1;
// /** waitStatus value to indicate thread is waiting on condition */
// static final int CONDITION = -2;
// /**
// * waitStatus value to indicate the next acquireShared should
// * unconditionally propagate
// */
// static final int PROPAGATE = -3;
// 当前置节点状态为single时 ,则需要唤醒(首次进来时前置节点状态默认为0)
if (ws Node.SIGNAL){
/*
* This node has already set status asking a release
* to signal it, so it can safely park.
*/
return true;
}
// 节点状态大于0只有一种情况,即CANCELLED
// 将CANCELLED状态的节点丢掉
if (ws > 0) {
/*
* Predecessor was cancelled. Skip over predecessors and
* indicate retry.
*/
do {
// 相当于 pred = pred.prev ;node.prev = pred;
node.prev = pred = pred.prev;
} while (pred.waitStatus > 0);
pred.next = node;
} else {
/*
* waitStatus must be 0 or PROPAGATE. Indicate that we
* need a signal, but don't park yet. Caller will need to
* retry to make sure it cannot acquire before parking.
*/
// 标注前一个节点的状态为single
compareAndSetWaitStatus(pred, ws, Node.SIGNAL);
}
return false;
}
private final boolean parkAndCheckInterrupt() {
// 挂起当前线程
LockSupport.park(this);
// 如果当前线程有被中断过 返回true
// 线程被挂起时,是无法响应中断操作的,当被执行unPark()唤醒后响应中断
return Thread.interrupted();
}
// *******************************************************************************************************
lock.unlock();
// sync.class
public void unlock() {
sync.release(1);
}
// 释放锁
// AQS.class
public final boolean release(int arg) {
if (tryRelease(arg)) {
Node h = head;
if (h != null && h.waitStatus != 0)
unparkSuccessor(h);
return true;
}
return false;
}
Sync.class
// 尝试进行释放锁,因为lock锁是可重入的,所以如果有多次获得锁,就需要多次去释放锁
protected final boolean tryRelease(int releases) {
int c = getState() - releases;
if (Thread.currentThread() != getExclusiveOwnerThread())
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
boolean free = false;
// 当重入次数为0是,真正的是否锁,设置拥有锁的线程为null
if (c 0) {
free = true;
setExclusiveOwnerThread(null);
}
// 设置线程状态
setState(c);
return free;
}
// 唤醒挂起的线程
private void unparkSuccessor(Node node) {
/*
* If status is negative (i.e., possibly needing signal) try
* to clear in anticipation of signalling. It is OK if this
* fails or if status is changed by waiting thread.
*/
int ws = node.waitStatus;
if (ws < 0)
compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, ws, 0);
/*
* Thread to unpark is held in successor, which is normally
* just the next node. But if cancelled or apparently null,
* traverse backwards from tail to find the actual
* non-cancelled successor.
*/
// 从后往前,删除无效节点
Node s = node.next;
if (s null || s.waitStatus > 0) {
s = null;
for (Node t = tail; t != null && t != node; t = t.prev)
if (t.waitStatus <= 0)
s = t;
}
// 唤醒线程
if (s != null)
LockSupport.unpark(s.thread);
}
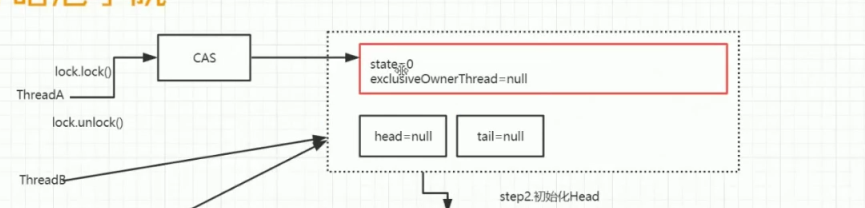
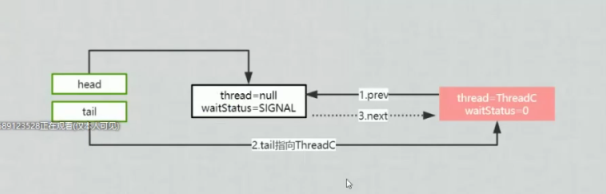
多个线程争夺锁过程
Lock
 ###
###
unLock
公平锁和非公平锁区别
Lock锁非公平锁在实现层面会多次通过tryAcquire()尝试获取锁,如果能拿到锁,就会直接插队,
而公平锁在tryAcquire()方法中,则会通过hasQueuedPredecessors 校验 避免插队
线程中断回顾
- thread.interrupt() 中断线程
- boolean Thread.interrupted() 获取中断状态/复位(默认false)
- boolean Thread.cucurrentThread.isInterrupted() 线程是否有中断过
ReentrantLock和Synchronized的区别
- synchronized是关键字 reentrantLock是juc包下的类
- synchronized 只有在代码执行完毕或者发生异常的情况下才能释放锁 lock通过unlock释放锁
- lock锁使用更加灵活
- lock锁可通过tryLock校验 避免死锁的发生
- lock锁可实现公平锁,默认非公平。synchronized为非公平锁





