CountDownLatch 主要的使用场景为计数器。
在整个过程中会用到AQS的共享锁
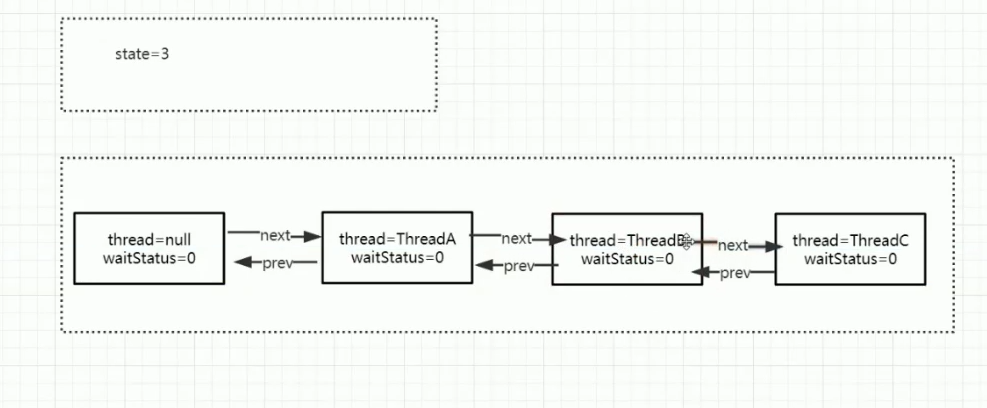
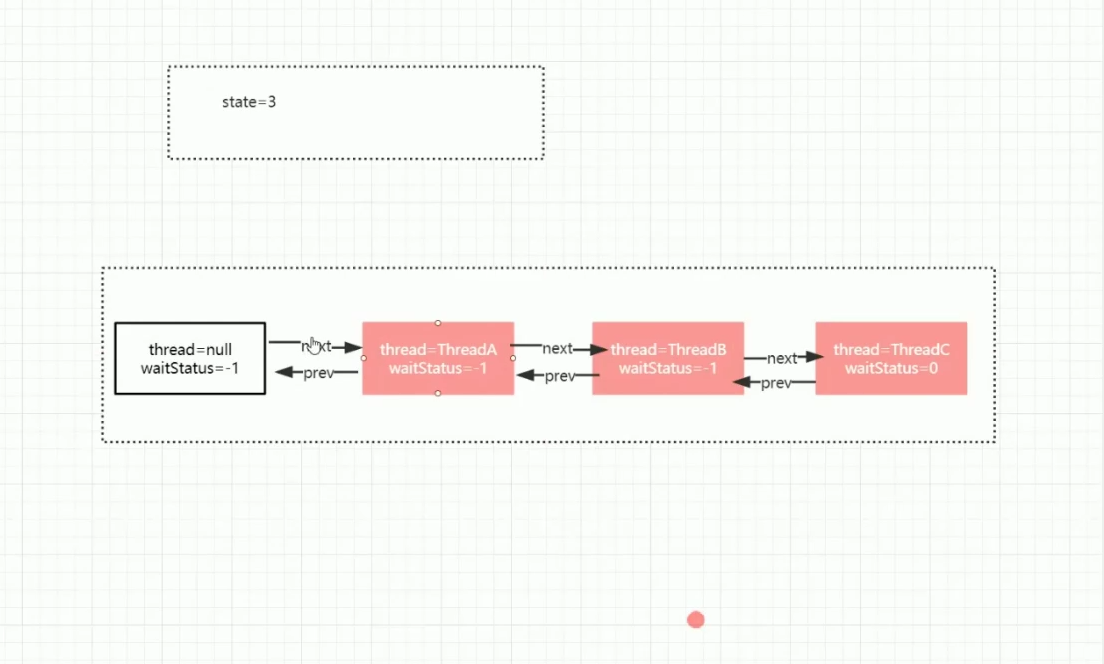
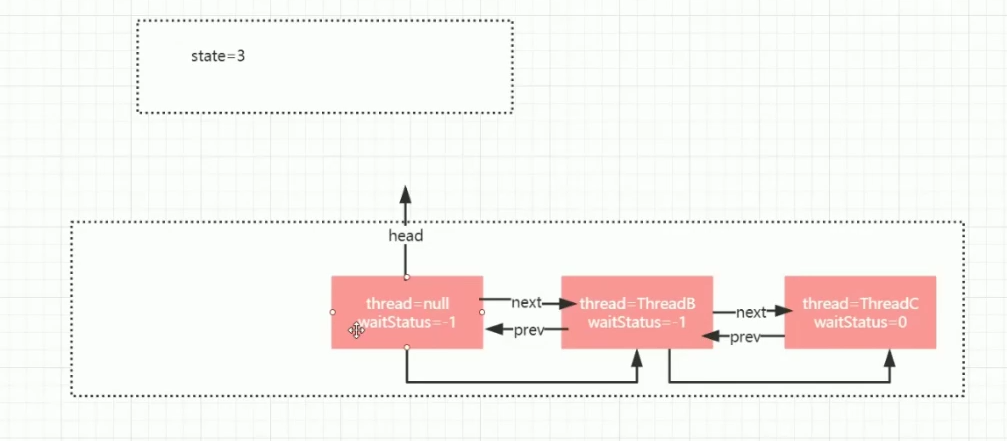
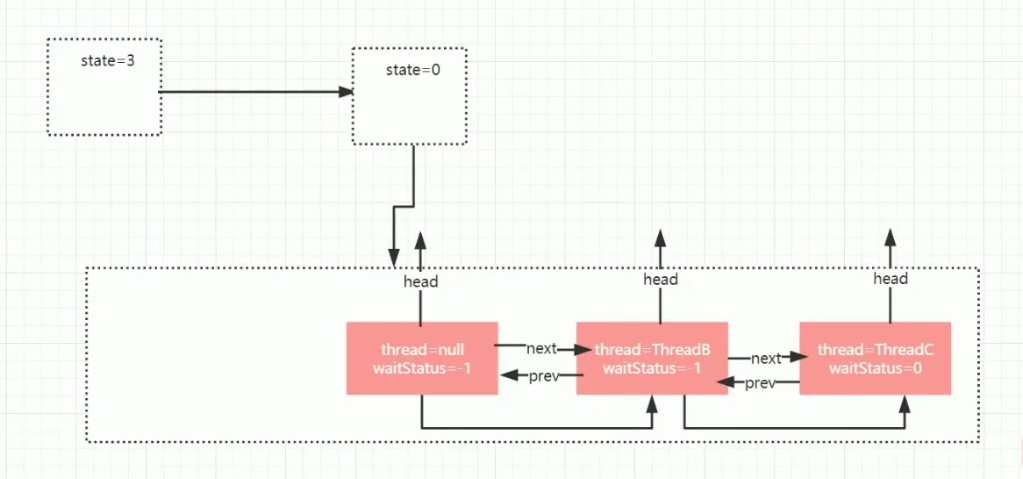
CountDownLatch中的state标识计数器的数值。 ## 计数器demo ```java /** * @PackageName: com.raven.multithreaded.concurrentutil.countdownlatch * @ClassName: CountDownLatchTest * @Blame: raven * @Date: 2021-09-01 14:00 * @Description: countdownlatch减数计数器 await阻塞到countDown计数为0后执行后续逻辑 */ public class CountDownLatchTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
// 定义一个countdownlatch计数器
CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(3);
new Thread(() -> {
// countdownlatch 计数-1
countDownLatch.countDown();
System.out.println("thread 1");
}).start();
new Thread(() -> {
// countdownlatch 计数-1
countDownLatch.countDown();
System.out.println("thread 2");
}).start();
new Thread(() -> {
// countdownlatch 计数-1
countDownLatch.countDown();
System.out.println("thread 3");
}).start();
// 阻塞线程 当countdownlatch state计数减少到0 执行await后的逻辑
countDownLatch.await();
System.out.println("countdownlatch state 为0,执行业务逻辑");
} }
## 模拟并发Demo
```java
/**
* @PackageName: com.raven.multithreaded.concurrentutil.countdownlatch
* @ClassName: CountDownLatchTest2
* @Blame: raven
* @Date: 2021-09-01 14:26
* @Description:模拟并发,使用await阻塞多个线程,当countDown计数为0后统一执行wait后逻辑
*/
public class CountDownLatchTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(1);
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
try {
// 阻塞多个线程
countDownLatch.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("thread:" +Thread.currentThread().getName());
}).start();
}
// 释放阻塞
countDownLatch.countDown();
}
}
public class CountDownLatchDemo{
// countDownLatch.await();
// Sync.class
public void await() throws InterruptedException {
// 获取共享锁,并且是可中断的
sync.acquireSharedInterruptibly(1);
}
// AQS
public final void acquireSharedInterruptibly(int arg) throws InterruptedException {
// 如果线程有被中断过,抛出异常
if (Thread.interrupted())
throw new InterruptedException();
// 尝试获取共享锁
if (tryAcquireShared(arg) < 0){
// 初始化后,因为为调用countDown 所以需要执行获取可中断共享锁
doAcquireSharedInterruptibly(arg);
}
}
// 尝试获取共享锁
protected int tryAcquireShared(int acquires) {
// state代表计数的值,当调用countDown后state减小
return (getState() == 0) ? 1 : -1;
}
private void doAcquireSharedInterruptibly(int arg) throws InterruptedException {
// 使用共享的方式 将当前线程封装为节点构建AQS队列,并将节点添加到AQS队列中
final Node node = addWaiter(Node.SHARED);
boolean failed = true;
try {
for (;;) {
// 获取当前节点的上一个节点
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head) {
int r = tryAcquireShared(arg);
if (r >= 0) {
setHeadAndPropagate(node, r);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return;
}
}
// 通过自旋的方式获取共享锁 然后挂起当前线程
// 如果获取锁后当前线程有被中断过,则抛出中断异常响应中断
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt())
throw new InterruptedException();
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
// countDownLatch.countDown();
// sync.class
// 释放共享锁
public void countDown() {
sync.releaseShared(1);
}
public final boolean releaseShared(int arg) {
// 当多个线程执行countDown 将state减为0后 执行释放锁的逻辑
if (tryReleaseShared(arg)) {
// 释放锁
doReleaseShared();
return true;
}
return false;
}
// 通过自旋的方式 cas的设置state的值 每次为state-1
protected boolean tryReleaseShared(int releases) {
// Decrement count; signal when transition to zero
for (;;) {
int c = getState();
if (c == 0){
return false;
}
int nextc = c-1;
if (compareAndSetState(c, nextc)){
return nextc == 0;
}
}
}
private void doReleaseShared() {
for (;;) {
Node h = head;
if (h != null && h != tail) {
int ws = h.waitStatus;
//
if (ws == Node.SIGNAL) {
// 因为通过await后 所有线程状态都为-1
// 所以cas失败后,不进行唤醒挂起的线程
if (!compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, Node.SIGNAL, 0))
continue; // loop to recheck cases
// 唤醒挂起的线程
unparkSuccessor(h);
}
else if (ws == 0 &&
!compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, 0, Node.PROPAGATE))
continue; // loop on failed CAS
}
if (h == head) // loop if head changed
break;
}
}
// ******************************线程被唤醒后****************************************************
/**
*
* 线程被唤醒后,释放了共享锁,doAcquireSharedInterruptibly继续执行自旋的逻辑
*
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head) {
// 此时已经通过countDown将state减为0
// r=1 r>0
int r = tryAcquireShared(arg);
if (r >= 0) {
setHeadAndPropagate(node, r);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return;
}
}
*/
protected int tryAcquireShared(int acquires) {
return (getState() == 0) ? 1 : -1;
}
// 传播的将当前线程设置为head 并唤醒下一个节点,传播的唤醒 释放共享锁
private void setHeadAndPropagate(Node node, int propagate) {
Node h = head; // Record old head for check below
setHead(node);
if (propagate > 0 || h == null || h.waitStatus < 0 ||
(h = head) == null || h.waitStatus < 0) {
// 获取下一个节点
Node s = node.next;
// 传播的唤醒下一个节点,进行释放锁
if (s == null || s.isShared())
doReleaseShared();
}
}
}
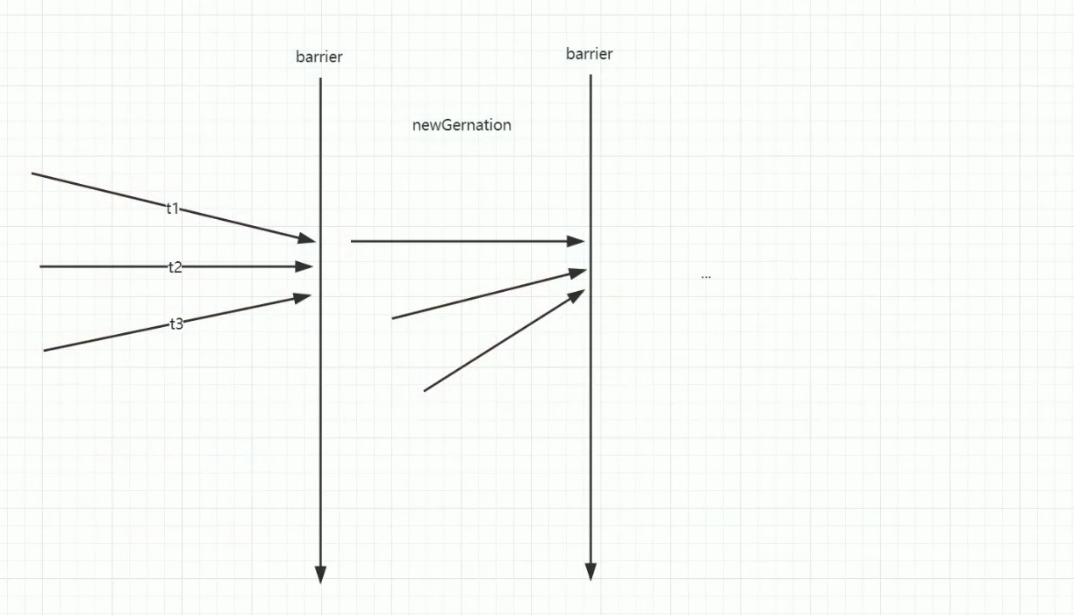
CyclicBarrier 中state标识栅栏的数值 也采用的是AQS的共享锁 ## CyclicBarrierDemo 模拟所有文件上传完毕后进行数据分析 ```java /** * @PackageName: com.raven.multithreaded.concurrentutil.cyclicbarrier * @ClassName: CyclicBarrierTest * @Blame: raven * @Date: 2021-09-01 18:45 * @Description: cyclicBarrierDemo 循环栅栏 * 模拟文件上传 等待所有文件上传后,才执行指定逻辑 */ public class CyclicBarrierTest extends Thread {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 指定栅栏的个数 当有三个文件上传后,次进行数据分析
// 第一个参数: 指定满足栅栏的个数
// 第二个参数: 满足后所需要执行的逻辑
CyclicBarrier cyclicBarrier = new CyclicBarrier(3, new CyclicBarrierTest());
new Thread(new DataImportThread("file1", cyclicBarrier)).start();
new Thread(new DataImportThread("file2", cyclicBarrier)).start();
new Thread(new DataImportThread("file3", cyclicBarrier)).start();
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("所有文件上传完毕,开始数据分析");
}
static class DataImportThread extends Thread {
private String path;
private CyclicBarrier cyclicBarrier;
public DataImportThread(String path, CyclicBarrier cyclicBarrier) {
this.path = path;
this.cyclicBarrier = cyclicBarrier;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
// 文件上传后阻塞
System.out.println("开始导入文件,已导入" + path + "的文件");
cyclicBarrier.await();
} catch (InterruptedException | BrokenBarrierException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
} } ```
public class CyclicBarrierDemo{
// cyclicBarrier.await();
// CyclicBarrier.class
public int await() throws InterruptedException, BrokenBarrierException {
try {
return dowait(false, 0L);
} catch (TimeoutException toe) {
throw new Error(toe); // cannot happen
}
}
// 执行阻塞
// 基于Lock锁 以及condition 完成阻塞操作
private int dowait(boolean timed, long nanos) throws InterruptedException, BrokenBarrierException,TimeoutException {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
final Generation g = generation;
if (g.broken)
throw new BrokenBarrierException();
// 如果线程有被中断过,则终止barrier 并抛出异常
if (Thread.interrupted()) {
breakBarrier();
throw new InterruptedException();
}
// count为构建栅栏时指定的突破栅栏需要的次数
int index = --count;
if (index == 0) { // tripped
boolean ranAction = false;
try {
// 如果构造参数有传突破栅栏后的命令,则执行命令
final Runnable command = barrierCommand;
if (command != null)
command.run();
ranAction = true;
// 重置栅栏参数
nextGeneration();
return 0;
} finally {
if (!ranAction)
breakBarrier();
}
}
// loop until tripped, broken, interrupted, or timed out
for (;;) {
try {
if (!timed)
// 阻塞线程
// 基于condition的await进行阻塞挂起线程
trip.await();
else if (nanos > 0L)
// 延时阻塞
nanos = trip.awaitNanos(nanos);
} catch (InterruptedException ie) {
if (g == generation && ! g.broken) {
breakBarrier();
throw ie;
} else {
// We're about to finish waiting even if we had not
// been interrupted, so this interrupt is deemed to
// "belong" to subsequent execution.
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}
if (g.broken)
throw new BrokenBarrierException();
// 当突破栅栏后 会构建新的generation 此时 g != generation 终止循环
if (g != generation)
return index;
if (timed && nanos <= 0L) {
breakBarrier();
throw new TimeoutException();
}
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
private void nextGeneration() {
// signal completion of last generation
trip.signalAll();
// set up next generation
count = parties;
generation = new Generation();
}
}